Optimization of Game Performance in Low-end Devices: Tips, Tricks, and Smart Workarounds
Optimization of Game Performance in Low-end Devices: Tips, Tricks, and Smart Workarounds
Image Courtesy: Headspin.io
The mobile gaming market is growing rapidly, especially in regions where low-end devices dominate. According to Omdia, phones under $150 grew by 33% year-over-year, with ultra-budget models (under $90) seeing 87% growth in Q1 2024 alone. Optimizing your game for low-end hardware isn’t just a good idea; it’s essential. In this blog, we’ll explore practical techniques to enhance game performance across graphics, memory, and frame rate; ensuring smooth gameplay even on older or budget devices.
Ensuring games run smoothly on low-end hardware is crucial for maintaining a wide and inclusive player base.
A recent survey by the Omdia group reports that the demand for low-end devices is increasing rapidly year on year. The survey reveals that phones priced below $150 experienced significant growth, increasing by 30 million year-over-year from 90 million in Q1 2023 to 120 million in Q1 2024, representing a 33% rise!
Ultra-low-cost phones, priced under $90, saw an 87% growth. As a result, this surge reflects rising demand in budget segments, jumping from 18 million units in Q1 2023 to 34 million in Q1 2024.
The image below represents the number of mobile devices sold from Q4-21 to Q1-24, with respect to their price.
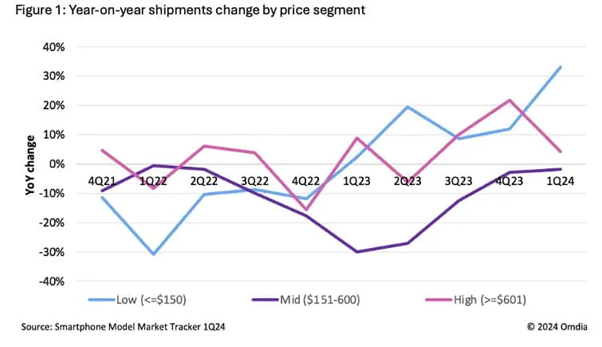
Image courtesy: omdia.tech.informa.com
The survey clearly states that the preference for low-end devices is increasing year by year. Therefore, for an application or a game to succeed and stay in the long run, optimizing it for this growing user base is crucial.
Here we will explore the key techniques for optimizing game performance on low-end devices, the tricks and smart practices, and the benefits and trade-offs developers need to consider.
What are Low-End Devices?
Low-end devices generally refer to computers or mobile devices with limited processing power, limited RAM, and older graphics capabilities, making them less capable of running demanding modern games smoothly.
These devices often struggle with high-resolution textures, complex physics simulations, and other resource-intensive features found in newer games.
Need for Low-End Device Optimization:
Optimizing games for better performance on low-end devices is crucial in today’s competitive gaming market. Otherwise, if the game performance does not meet expectations, it can lead to serious consequences such as negative reviews or, in the worst case, uninstalls.
Optimization does not mean only reducing lag and crashes in gameplay. It does mean that the user should feel engaged by providing an immersive gaming experience. This will help us in better ranking our game in the Play Store/App Store, leading to potential revenue.
It allows more players to enjoy the game, regardless of their device’s capabilities, leading to increased engagement and potential revenue.
Optimization of games for low-end devices helps in accomplishing,
Wider audience reach:
Optimizing for lower specifications allows developers to reach a broader player base, including those in emerging markets or with older devices.
In addition, well-optimized games are accessible to a wider range of players, even those using older devices.
Enhanced user experience:
Games that are fine-tuned for low-end devices run smoother, with fewer crashes and less lag, even on such devices, leading to a more enjoyable and engaging experience for players.
Better overall performance:
Techniques like reducing draw calls, using optimized shaders, and employing level of detail (LOD) systems can improve performance across all devices, and in addition, they benefit low-end devices the most.
Increased revenue potential:
Reaching a larger audience through optimization can translate to increased revenue and monetization opportunities.
Characteristics:
Below are some of the characteristics which challenges the optimization in low end devices.
- Limited processing power
- Low RAM capacity
- Basic Graphics Processing Units
- Lower screen resolution
- Limited internal storage
- Limited battery life
- Thermal throttling
Game Performance Optimization Techniques:
Before we start optimizing our game for low-end devices, we must learn what areas should be focused on. Some crucial aspects of optimization are game graphics, resource management, optimizing the code, better memory management, battery optimization, etc.
Let us see them in brief here:
Graphics Optimization
Reduced resolution and texture quality: Scaling down the game resolution to 720p or lower significantly reduces GPU load. This helps in providing users with engaging, lag-free, and crash-free gaming.
Level of Detail (LOD) scaling: It is a technique used to optimize game performance by adjusting the complexity of 3D models dynamically, based on their distance from the camera.
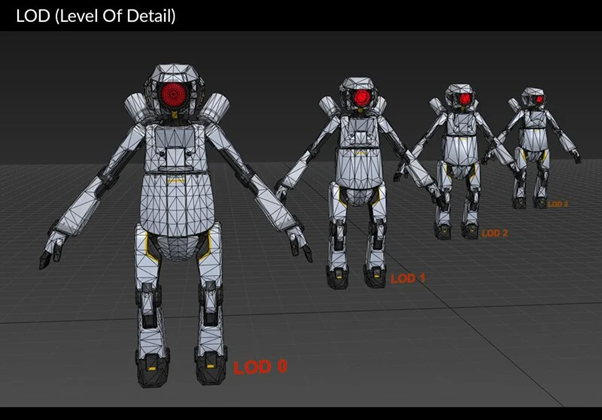
Image courtesy: developer.android.com
Simpler, less detailed versions of objects are rendered when they are far away, while higher-detail versions are used when they are closer, thus saving processing power without significantly impacting visual quality.
Simplified shaders: Programs that are responsible for rendering and manipulating the visuals of a game are called shaders.
In addition, simplifying shaders involves optimizing their complexity and performance to ensure smooth rendering and visual fidelity by using practices like lower precision data types, reducing branching, and reusing code.
Dynamic Resolution Scaling (DRS): It is a technique used in real-time rendering. The game engine automatically scales the resolution up and down to have a smooth performance.
It helps to maintain stable frame rates during demanding scenes, thus improving the gaming experience.
Efficient Resource Management
Memory Optimization:
Efficient memory management is crucial for the stable performance of games. Techniques like asset streaming and reducing active game objects help prevent crashes and reduce lag.
Some of the techniques used for efficient memory management are,
Memory pooling: Reuse objects that frequently appear and disappear during the game (like projectiles or minor enemies) instead of repeatedly creating and deleting them. This reduces the overhead of memory allocation and garbage collection.
Memory profiling: Developers should profile the game’s memory usage at regular intervals during development to identify and address memory leaks or excessive memory consumption.
Asset Streaming
For instance, asset streaming enables a game to load only the needed components of the game world.”on the fly” as required, which helps in significantly reducing the initial load times and overall memory usage.
Asynchronous Loading: This technique involves loading assets in the background asynchronously without freezing the game.
It improves the user experience by reducing perceived load times and preventing gameplay interruptions.
Segmentation and Prioritization: It is the practice of dividing the assets of a game into segments and prioritizing their loading based on the player’s current state and position.
This method ensures that resources are managed smartly and available when most needed.
Frame Rate Stabilization
Maintaining a stable frame rate is essential for ensuring seamless gameplay. Fluctuations in frame rate can interrupt the gaming experience and lead to visual stuttering.

Image courtesy: 100ms.live
Rendering paths: Developers simplify rendering paths by reducing draw calls and optimizing the scene graph to stabilize the frame rate.
Making use of culling techniques to avoid rendering objects (that are not visible to the player) also helps in achieving a stable frame rate.
Fixed time step: It is a method in game development where physics and other game logic updates are performed at a predetermined, consistent interval, regardless of the actual frame rate of the game.
This means that even if the game’s rendering slows down, the physical computations will still happen at the same rate, leading to more predictable and stable gameplay.
GPU and CPU Optimization
Optimizing GPU & CPU by balancing the load between the GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) and CPU (Central Processing Unit) can significantly enhance performance, particularly in graphics-intensive games.
Profile GPU and CPU Usage:
Profiling CPU and GPU involves analyzing the performance of our application on both the central processing unit (CPU) and the graphics processing unit (GPU) to identify bottlenecks and optimize performance.
CPU profiling focuses on the execution time of different functions and how they utilize CPU resources.
CPU load, memory usage, clock speed, and instructions per cycle (IPC) are some of the metrics used in CPU profiling.
Profilers like Visual Studio Profiler, N|Solid (Node.js), and pprof (Go) are used to analyze CPU performance.
GPU profiling examines the rendering pipeline and how the GPU handles graphics tasks.
Metrics like GPU utilization, memory utilization, rendering time per stage, and overdraw (when a pixel is drawn multiple times) are crucial in GPU profiling.
Android’s Profile GPU Rendering, NVIDIA Nsight Systems, and NVIDIA Nsight Compute are some of the tools used in analyzing the GPU performance.
Combined Profiling (CPU and GPU):
Developers use combined CPU and GPU profiling to analyze performance and identify bottlenecks across both processors.
This approach allows developers to understand how these two components interact and where delays or inefficiencies occur within the system.
Combining CPU and GPU profiling helps in identifying:
Bottlenecks: By combining data, developers can pinpoint whether a problem is CPU-bound (CPU is the bottleneck), GPU-bound (GPU is the bottleneck), or transfer-bound (data transfer between CPU and GPU is the bottleneck).
Understanding CPU-GPU Interactions: Combined profiling reveals how the CPU and GPU coordinate, highlighting potential delays in transferring data or launching GPU kernels.
Timing captures in tools like Pix (Microsoft) combine CPU and GPU data, allowing for a holistic view of application performance.
Multithreading: Utilize multithreading to distribute game logic, rendering, and other tasks across multiple CPU cores, thus reducing the load on any single core and improving overall performance.
Code Optimization
Optimizing the game code is crucial to ensure smooth performance on all possible hardware configurations.
Algorithms and data structures: By using the algorithms and data structures efficiently, the load on the CPU is reduced significantly.
For example, the game performance can be improved by the optimization of route-finding algorithms or by using more efficient sorting and search methods.
Network Optimization
Data compression: This technique minimizes bandwidth usage and improves latency by reducing data size during transmission.
Efficient usage of protocols: Leveraging UDP (User Datagram Protocol) over TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) can significantly reduce lag in real-time games.
Reducing the server load: Methods such as client-side prediction and interpolation lower the server load and enhance responsiveness in multiplayer scenarios.
Trade-offs in Optimization
Trade-offs in game optimization often revolve around the balance between performance, visual quality, and gaming experience.
Visual quality vs. performance: Lowering resolution, detail, and effects boosts performance but can reduce graphical fidelity.
Gameplay depth vs. resource use: Simplifying AI or physics can enhance performance but may impact immersion or challenge.
Feature set vs. compatibility: Advanced features like ray tracing may need to be omitted to maintain accessibility.
Battery life vs. processing power: On mobile devices, conserving battery may require limiting graphical and processing intensity. On the other hand, pushing performance too much can quickly drain the battery.
Case Studies
Fortnite (Epic Games)
Fortnite demonstrates scalable optimization, offering dynamic resolution, simplified shaders, and adjustable graphics settings.
On mobile devices, it automatically configures settings based on hardware capacity to maintain smooth gameplay.
PUBG Mobile (Tencent Games)
PUBG Mobile provides multiple graphical presets, supports asset streaming, and implements LOD scaling to optimize performance across a wide range of smartphones, including budget models.
Minecraft (Mojang Studios)
Minecraft’s minimalist block-style visuals inherently reduce GPU demands. The game includes settings for render distance and particle effects, making it playable on everything from PCs to entry-level phones.
Best Practices for Developers
Early and Regular Profiling
Developers should integrate performance profiling early in development to identify and resolve bottlenecks before they become critical.
Customizable Graphics Settings
Players should be allowed to tailor their experience by adjusting resolution, frame rate, effects, and more based on their device’s capabilities.
Real-time Testing
Real-world testing on low-end hardware is crucial, as emulators often fail to capture true performance characteristics.
When making trade-offs, always preserve the game’s core experience. Visual and technical sacrifices should not compromise the fun or functionality of the game.
Takeaways:
As the gaming industry continues to expand, inclusivity and accessibility have become more important than ever. Supporting low-end hardware not only increases the reach of a game but also reflects a commitment to delivering high-quality experiences to all players.
Optimizing game performance for low-end devices involves carefully balancing various techniques and trade-offs to ensure games remain accessible and enjoyable across a wide range of hardware configurations.
By prioritizing graphics optimization, efficient resource use, and streamlined code, developers can deliver smooth gameplay even on less powerful devices.
With the right strategies and a thoughtful approach, developers can successfully navigate the challenges of optimization and build engaging games that resonate with players, no matter what device they use.
Wrapping Up:
Planning and maintaining these strategies may seem difficult at first. However, there’s no need to worry. We at Xpress Gaming have an experienced team of developers and testers, and we provide you with best-in-class products and services for every aspect of the game development.
Our game development expertise in building creative and engaging games also helps the game to stand out in a competitive market. Click here to reach us and learn about our products and services. Happy gaming!
